
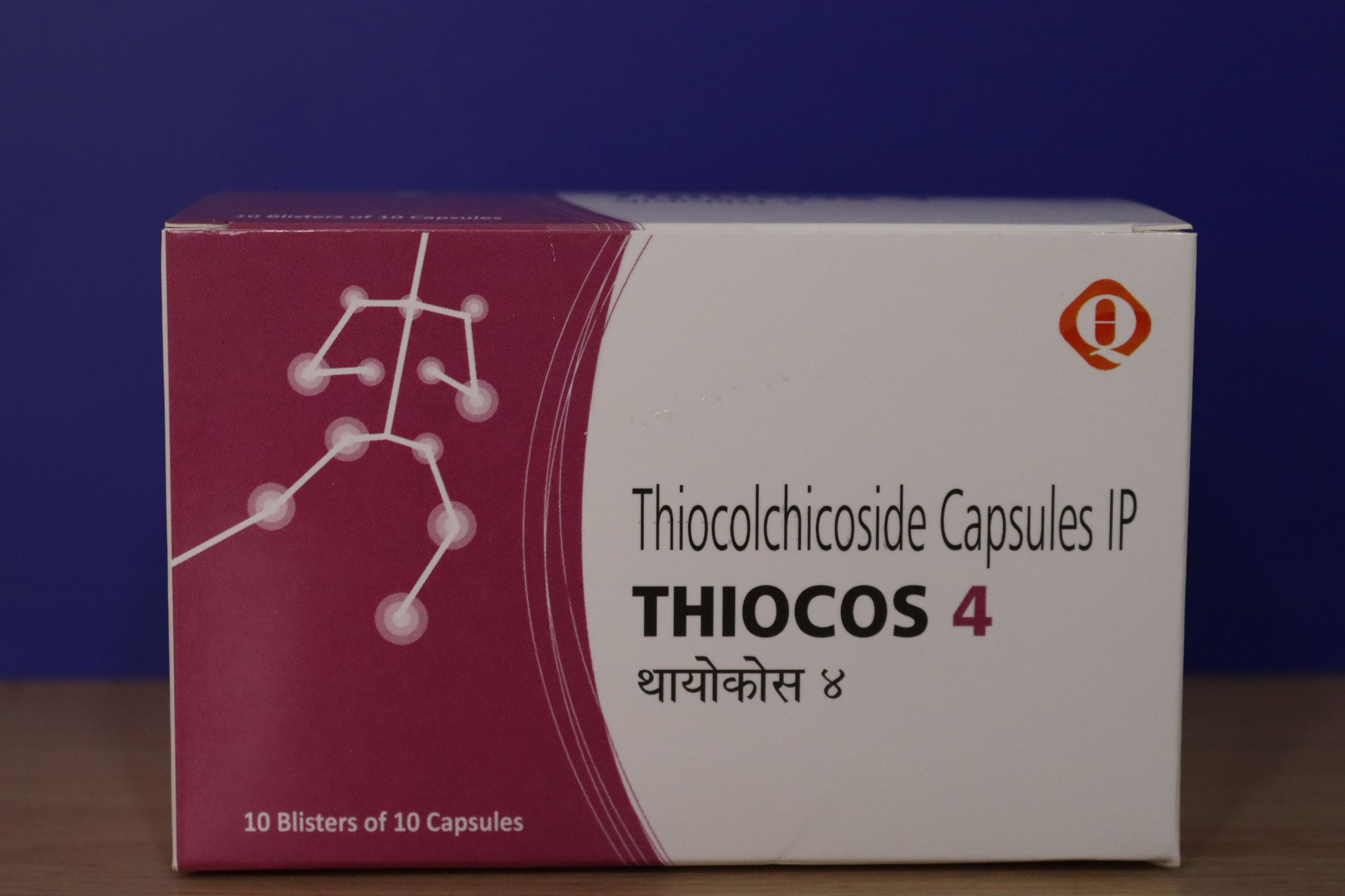
THIOCOS
Thiocolchicoside Capsule
Thiocolchicoside is a potent competitive γ-amino butyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor antagonist and glycine receptor agonist with muscle relaxant, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic activity.
PRESENTATION
Each Hard Gelatin Capsule Contains Thiocolchicoside 4 Mg IP.
Packing: Blister
Pack Size: 10*10
CLINICAL PARTICULARS
Therapeutic Indications
Posology and Method of Administration
Posology
For the oral form 4 mg and 8 mg:
The recommended and maximal dose is 8 mg every 12 hours (i.e. 16 mg per day). The treatment duration is limited to 7 consecutive days.
Doses exceeding recommended doses or long-term use should be avoided.
Pediatric Population
Thiocos should not be used in children and adolescents under 16 years of age because of safety concerns.
Method of Administration
Oral administration with glass of water.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Thiocolchicoside Must Not Be Used:
Special Warnings and Precautions for Use
Preclinical studies showed that one of thiocolcoside metabolites induced aneuploidy
(i.e. unequal number of chromosomes in dividing cells) at concentrations close to human exposure observed at doses 8 mg twice daily. Aneuploidy is considered as a risk factor for teratogenicity, embryo/foeto-toxicity, spontaneous abortion, and impaired male fertility and a potential risk factor for cancer. As a precautionary measure, use of the product at doses exceeding the recommended dose or long-term use should be avoided.
Patients should be carefully informed about the potential risk of a possible pregnancy and about effective contraception measures to be followed.
Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation
Pregnancy
There are limited data on the use of thiocolchicoside in pregnant women. Therefore, the potential hazards for the embryo and fetus are unknown. Studies in animals have shown teratogenicity effects.
Thiocos is contraindicated during pregnancy and in women of childbearing potential not using contraception.
Breastfeeding
Since it passes into the mother’s milk, the use of thiocolchicoside is contraindicated during breastfeeding.
Fertility
In a fertility study performed in rats, no impairment of fertility was seen at doses up to 12 mg/kg, i.e. at dose levels inducing no clinical effect. Thiocolchicoside and its metabolites exert an eugenic activity at different concentration levels, which is a risk factor for impairment of human fertility.
UNDESIRABLE EFFECTS
Adverse events are classified per frequency as follows: Very Common (≥1/10), Common (≥1/100 and <1/10), Uncommon (≥1/1000 and <1/100), Rare (≥1/10000 and <1/1000), Very Rare (<1/10000), not known (cannot be estimated from the available data).
Immune System Disorders
Rare: Hypersensitivity reactions such as urticaria.
Frequency Unknown: Hypersensitivity reactions such as angioedema and, exceptionally, anaphylactic shock.
Frequency Unknown: Anaphylactic reactions.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Uncommon: Skin reactions such as pruritus, erythema, maculopapular eruptions and, exceptionally, vesiculobullous eruptions.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Common: Diarrhea, gastralgia.
Uncommon: Nausea, vomiting.
Hepatobiliary Disorders
Frequency Unknown: Hepatic conditions (such as cytolytic or cholestasis hepatitis).
Nervous System Disorders
Common: Drowsiness.
Frequency Unknown: Seizure or relapsed attack in epileptic patients.
PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
Pharmacodynamics properties
Pharmacotherapeutic Group: centrally acting myorelaxant.
Thiocolchicoside is a sulphur-containing, synthetic analogue of a natural colchicum glycoside which behaves pharmacologically as a muscle relaxant, both in humans and in animals. It eliminates, or substantially decreases, centrally originating muscle contracture: in spastic hypertonia, it reduces the muscle’s passive resistance to stretching and decreases, or removes, the residual contracture. Its muscle-relaxing effect can also be observed on the visceral muscles: it has, in particular, been demonstrated on the uterus. However, thiocolchicoside has no curariform effect, since it acts through the central nervous system rather than paralyzing the muscle’s motor plaque.
Mode of Action: research conducted in 2003 and 2007 has shown that its myorelaxant activity may be caused by an agonist action on the glycine receptors located primarily in the brain stem and the spinal cord. Thiocolchicoside does not, therefore, impair voluntary motility or cause paralysis, and thus is devoid of any respiratory risk. Thiocolchicoside has no influence on the cardiovascular system. Lastly, thiocolchicoside also acts as an antagonist of A-type GABA receptors (mainly located in the cerebral cortex), this pharmacological action being known to have convulsant or pro-convulsant properties.
Pharmacokinetic Properties
Absorption
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of thiocolchicoside is estimated around 42.7 L after an IM administration of 8 mg. No data are available for both metabolites.
Biotransformation
After oral administration, thiocolchicoside is first metabolized in the aglycon 3- demethyltiocolchicine or SL59.0955. This step mainly occurs by intestinal metabolism explaining the lack of circulating unchanged thiocolchicoside by this route of administration. SL59.0955 is then glucuroconjugated into SL18.0740 which has equipotent pharmacological activity to thiocolchicoside and thus supports the pharmacological activity after oral administration of thiocolchicoside. SL59.0955 is also demethylated into didemethyl-thiocolchicine.
Elimination
Preclinical Safety Data
Thiocolchicoside profile has been assessed in vitro, and in vivo following parenteral and oral administration.
Thiocolchicoside was well tolerated following oral administration for periods of up to 6 months in both the rat and the non-human primate when administered at repeated doses of less than or equal to 2 mg/kg/day in the rat and less or equal to 2.5 mg/kg/day in non-human primate, and by the intramuscular route in the primate at repeated doses up to 0.5 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks.
At high doses, thiocolchicoside induced emesis in dog, diarrhea in rat and convulsions in both rodents and non-rodents after acute administration by oral route.
After repeated administration, thiocolchicoside induced gastro-intestinal disorders (enteritis, emesis) by oral route and emesis by IM route.
Thiocolchicoside itself did not induce gene mutation in bacteria (Ames test), in vitro chromosomal damage (chromosome aberration test in human lymphocytes) and in vivo chromosomal damage (in vivo micronucleus in mouse bone marrow administered intraperitoneally).
The major glucuro-conjugated metabolite did not induce gene mutation in bacteria (Ames test); however it induced in vitro chromosomal damage (in vitro micronucleus test on human lymphocytes) and in vivo chromosomal damage (in vivo micronucleus test in mouse bone marrow administered orally). The micronuclei predominantly resulted from chromosome loss (centromere positive micronuclei after FISH centromere staining), suggesting an eugenic properties. An eugenic effect was observed at concentrations in the in vitro test and at AUC plasma exposures in the in vivo test higher (more than 10 fold based on AUC) than those observed in human plasma at therapeutic doses.
The aglycon metabolite (3-demethylthiocolchicine) formed mainly after oral administration induced in vitro chromosomal damage (in vitro micronucleus test on human lymphocytes) and in vivo chromosomal damage (in vivo oral micronucleus test in rat bone marrow administered orally). The micronuclei predominantly resulted from chromosome loss (centromere positive micronuclei after FISH or CREST centromere staining), suggesting a eugenic properties.
The an eugenic effect was observed at concentrations in the in vitro test and at exposures in the in vivo test close to those observed in human plasma at therapeutic doses of 8 mg twice daily per os. An eugenic effect in dividing cells may result in aneuploidy cells. Aneuploidy is a modification in the number of chromosomes and loss of heterozygosis, which is recognized as a risk factor for teratogenicity, embryo toxicity/ spontaneous abortion, impaired male fertility, when impacting germ cells and a potential risk factor for cancer when impacting somatic cells. The presence of the aglycon metabolite (3-demethylthiocolchicine- after intramuscular administration has never been assessed, therefore its formation using this route of administration cannot be excluded.
In the rat, an oral dose of 12 mg/kg/day of thiocolchicoside caused major malformations along with ototoxicity (retarded growth, embryo death, impairment of sex distribution rate). The dose without toxic effect was 3 mg/kg/day.
In the rabbit, thiocolchicoside showed maternotoxicity starting from 24 mg/kg/day. Furthermore, minor abnormalities have been observed (supernumerary ribs, retarded ossification).
In a fertility study performed in rats, no impairment of fertility was seen at doses up to 12 mg/kg/day, i.e. at dose levels inducing no clinical effect. Thiocolchicoside and its metabolites exert an eugenic activity at different concentration levels, which is recognized as a risk factor for impairment of human fertility. The carcinogenic potential was not evaluated.
Special Precautions for Storage
Do not store above 30°C.