
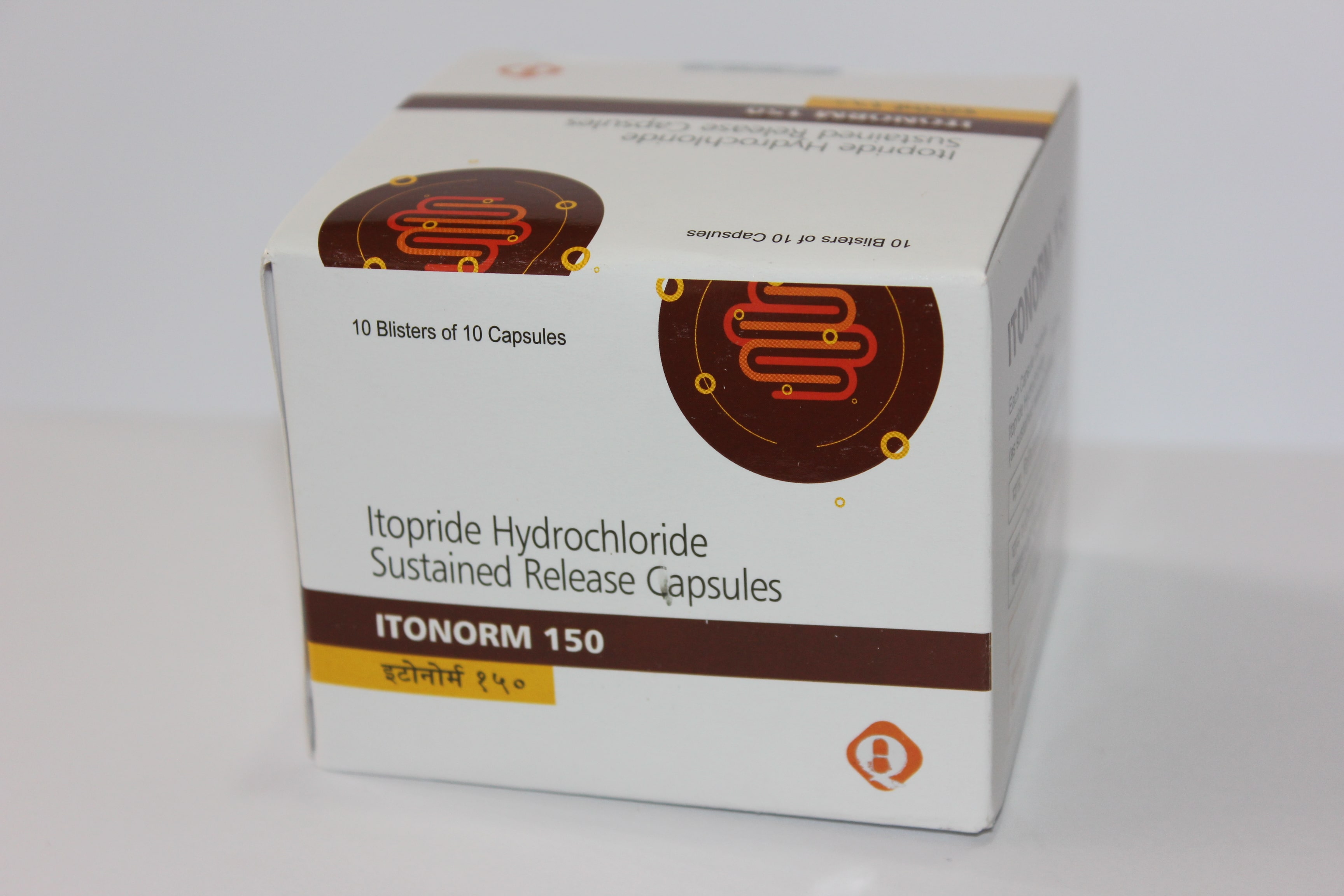
ITONORM
Itopride Hydrochloride 50mg SR Capsules
Itopride Hydrochloride 50 mg Tablets
The Active Ingredient of ITONORM is Itopride Hydrochloride, Drugs for functional gastrointestinal disorders. Which improves motility (automatic bowel and stomach movements, which are necessary to pass food through Digestive tract) and prevent from Nausea and Vomiting.
PRESENTATION
Each Capsule Contains Itopride Hydrochloride 150mg.
Each Tablets Contains Itopride Hydrochloride 50 mg
Pack Size: 10*10 Blisters.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacodynamics properties
Pharmacotherapeutic Group: Drugs for functional Gastrointestinal Disorders.
Mechanism of Action: Itopride activates the gastrointestinal propulsive motility by Dopamine D2 receptors Antagonistic action and Acetylcholine Esterase inhibitory action. Itopride activates Acetylcholine release and inhibits its degradation.
In addition Itopride has an Antiemetic effect which is based on interaction with Dopamine D2 receptors in Chemoreceptor zone. This effect was demonstrated by dose dependent inhibition of Apo Morphine induced vomiting in dogs. Itopride accelerates Stomach Emptying in Humans.
In animal studies in dogs with a single dose administration Itopride supported Stomach emptying. Itopride has high specific action in upper part of Gastrointestinal Tract. Itopride does not influence plasma concentrations of Gastrin.
Pharmacokinetic properties
Absorption: Itopride is absorbed rapidly and almost completely from Gastrointestinal Tract. Relative bioavailability is about 60% due to first-pass effect. Food does not affect bioavailability of the medicinal product. Maximum plasma concentrations are reached in 30 to 50 minutes after administration of 50 mg of Itopride. After repeated administration of doses in the range of 50 to 200 mg 3 times a day for period of 7 days, Itopride and its metabolites have shown pharmacokinetics of linear type with minimal accumulation.
Distribution: About 96% of Itopride is bound to plasma proteins, mainly Albumin. Alpha-1-Acidglycoprotein accounts for less than 15% of binding.
In rats Itopride is distributed extensively in the tissues (Vdß = 6.1 l/kg) except for central nervous system; high concentrations are reached in Kidneys, Small Intestine, Liver, Adrenal Glands and Stomach. Protein binding in rats was lower than in Humans (78% vs. 96%). Penetration into the Central Nervous System was minimal. Itopride is excreted in milk of Lactating rats.
Metabolism: In humans, Itopride is extensively metabolized in Liver. Three metabolites were identified of which only one manifests minor activity without pharmacological significance (about 2 to 3% of Itopride effect). The main metabolite is N-oxide, which is product of oxidation of the tertiary Amine-N-Dimethyl group.
Itopride is metabolized by Flavine Mono oxygenase (FMO3). The amount and efficacy of human FMO Iso enzymes can be associated with genetic polymorphisms which can result in rare autosomal recessive condition known as Trimethylaminuria (fish odor syndrome). Biological half-life in patient’s withTrimethylaminuria can be longer.
Pharmacokinetic in vivo studies of CYP-mediated reactions did not prove inhibition or induction of CYP2C19 and CYP2E1 caused by Itopride. Administration of Itopride did not influence content of CYP or the activity of Uridine-Diphosphate-Glucuronyl Transferase.
Excretion: Itopride and its metabolites are primarily excreted by urine. The amount of excreted Itopride and N-oxide after oral single therapeutic dose to healthy volunteers was 3.7% and 75.4%, respectively. Half-life of Itopride is about 6 hours.
DRUG-DRUG INTERACTIONS
INDICATIONS
DOSAGE AND METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION
Pediatrics population: The safety and efficacy of Itopride in Pediatric population has not been established.
Patients with Hepatic or Renal Impairment: Itopride is metabolized in Liver and the primary way of Excretion is via Kidneys. Patients with Impaired Hepatic or Renal function taking this medicinal product should be carefully monitored and in case of adverse reactions it is necessary to take appropriate measures, e.g. reduction of the dose or discontinuation of the therapy.
Elderly: It was shown in clinical trials that the incidence of adverse effects in patients aged 65 years and older was not higher than in younger patients. Itopride should be administered in elderly with adequate caution because of increased incidence in Hepatic and Renal Function Disorders, concomitant disease or treatment with additional drugs. Elderly using this medicinal product should be monitored closely and in case of Adverse reactions appropriate measures, such as reduction of the dose or discontinuation of the treatment should be taken.
Method of Administration: Capsules or Tablets should be swallowed with a sufficient amount of liquid.
SIDE-EFFECTS
Common (may affects 1 in 10 People)
Uncommon (may affect less than 1 in 100 people)
Rare (may affect less than 1 in 1000 people)
Unknown (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
In case of production or excretion of milk from mammary gland besides breast-feeding (Galactorrhea) or enlargement of mammary gland in men (Gynecomastia) stop the treatment and contact your doctor.
WARNING AND PRECAUTIONS
Itopride potentiates Acetylcholine action and can induce side cholinergic effects. Data about long-term administration of Itopride is not available
CONTRAINDICATIONS