
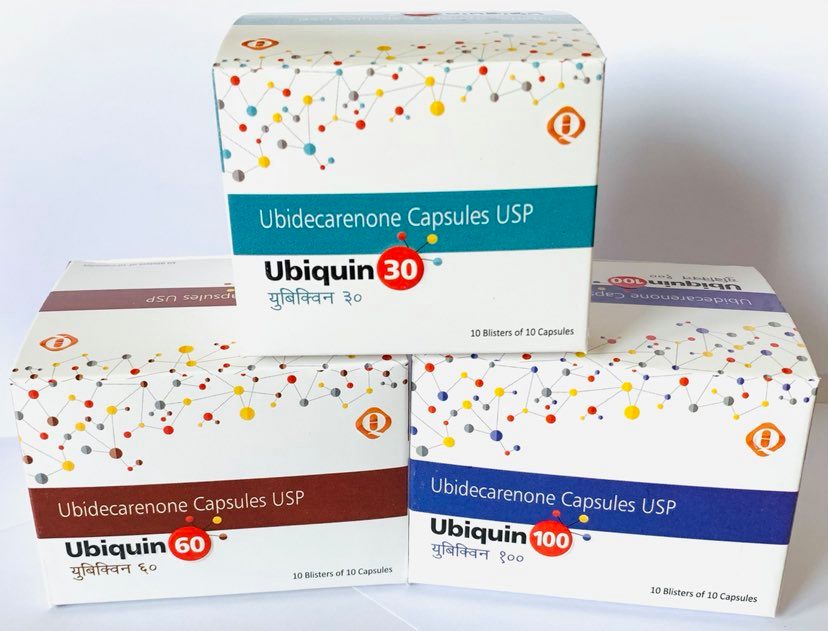
The active ingredient of UBIQUIN is Ubidecarenone, Ubidecarenone (Coenzyme Q10 is a vitamin-like substance), Anti-Oxidant.
Each Capsule Contains Ubidecarenone (Coenzyme Q10) /60mg/100mg.
Pack size: 10*10 Blisters.
Ubidecarenon has roles in many Physiological process including Sulfide Oxidation, regulation of Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore and Translocation of Protons and Calcium ions across Biological membranes. Studies have shown its beneficial effect in treating Cancer, Statin Myopathy, Congestive Heart Failure and Hypertension.
Mechanism of Action
Ubidecarenone is an essential cofactor in the Mitochondrial Electron transport chain. Its functions are the acceptance of electrons from the complex I and II and this activity is vital for the production of ATP. It acts as a mobile Redox agent shuttling electrons and protons in the electron transport chain. Ubidecarenone also presents Antioxidant activity in Mitochondria and Cellular membranes, Protecting against Peroxidation of Lipid membranes as well as inhibiting Oxidation of LDL-Cholesterol.
Ubidecarenone is absorbed from the Small Intestine into the Lymphatic and then it can enter the blood. The hydrophobicity and large molecular weight limit its absorption making it very poor and variable depending on the food intake and the number of Lipids presented in the food. The absorption is lower in the presence of an empty Stomach and greater in presence of high Lipid food diet. The daily dosage of Ubidecarenone presents the reach of maximal serum concentration by reaching a plateau after three weeks. The pharmacokinetic properties may vary between different brands but studies have reported an AUC of 11.51 mcg h/ml and a Cmax of 0.32 mcg/ml at a time of 7.9 h.
Ubidecarenone is distributed to the various tissues of the body and it is able to enter the brain. In preclinical studies with intravenous administration of Ubidecarenone, it is reported a volume of distribution of 20.4 L/kg which reflects its ability to penetrate extensively into organs and tissues. AS a general rule, tissues with high-energy requirements or metabolic activity tend to presents higher amounts of Ubidecarenone, these organs can be Heart, Kidney, Liver and Muscle.
In the blood, Ubidecarenone is split into the various Lipoprotein particles including LDL and VLDL.10 The plasma concentration of Ubidecarenone is highly dependent on the presence of plasma Lipoproteins and about 95% of the administered form is found in the reduced form.
Studies indicate that there is no saturation process during the metabolism of Ubidecarenone. It is metabolized in all tissues by the Phosphorylation in the cells and transportation to the Kidneys for further Excretion by the urine. After exerting its action, Ubidecarenone is reduced and forms Hydroquinone which is capable of recycling and regenerates other antioxidants such as Tocopherol and Ascorbate. The later metabolism of Hydroquinone generates the formation of Q acid I and Q acid II in free and conjugated forms.
The main Elimination route of Ubidecarenone is through the bile. After its oral administration, over 60% of the dose is excreted in the feces in the form of unchanged Ubidecarenone and a small fraction of the metabolites. In the urine, Ubidecarenone is bound to Saposin B protein and represents only 8.3% of the total administered dose.
The pharmacokinetic properties may vary between different brands but studies have reported a half-life of Ubidecarenone of 21.7 h.
In preclinical studies with intravenous administration of Ubidecarenone, it is reported a total clearance of 1.18 ml h/kg which was indicative of a prolonged Elimination.
Coenzyme Q-10 is an antioxidant. There is some concern that antioxidants might decrease the effectiveness of some medications used for cancers. But it is too soon to know if the interaction occurs.
Coenzyme Q-10 seems to decrease blood pressure. Taking Coenzyme Q-10 along with medications for high blood pressure might cause your blood pressure to go too low .Some medications for high blood pressure include Captopril, Enalapril ,Losartan Valsartan Diltiazem), Amlodipine, Hydrochlorothiazide, Furosemide and many others.
Warfarin is used to slow blood clotting. Coenzyme Q-10 might help the blood clot. By helping the blood clot, Coenzyme Q-10 might decrease the effectiveness of Warfarin. Decreasing the effectiveness of Warfarin might increase the risk of clotting. Be sure to have your blood checked regularly. The dose of your Warfarin might need to be changed.
Taking Coenzyme Q10 by mouth seems to improve symptoms of Coenzyme Q10 deficiency. This is a very rare condition. The symptoms include weakness, Fatigue, and Seizures.
Taking Coenzyme Q10 by mouth seems to reduce symptoms of Mitochondrial Disorders. However, improvement in symptoms is slow. Some people have to take Coenzyme Q10 for 6 months to get the most benefit.
Taking a specific product containing coenzyme Q-10, Acetyl-L-Carnitine, and Omega-3 Fatty Acids by mouth seems to improve vision in people with age-related vision loss.
Taking coenzyme Q10 along with Selenium might reduce the chance of Heart-related death in the elderly. It is not known if the same benefit might be seen in people living in other countries.
Early research found that Heart Failure might be linked with low Coenzyme Q10 levels. Some research shows that taking Coenzyme Q10 might help reduce some symptoms of Heart Failure. Coenzyme Q10 might also might reduce the chances of having an abnormal Heart Rhythm, Death, or hospitalization related to Heart Failure.
Research shows that taking Coenzyme Q-10 improves Nerve damage and Nerve pain in people with Nerve damage caused by Diabetes.
Some research show that taking Coenzyme Q10 by mouth seems to reduce pain by over 50%, Fatigue by 47%, morning tiredness by 56%, and tender points by 44% in people with Fibromyalgia.
Taking coenzyme Q10 by mouth seems to improve immune function in people with HIV/AIDS.
Reduced blood supply during Heart or Blood Vessel Surgery can deprive tissue of Oxygen. When blood supply returns to this tissue, the tissue can become damaged. There is some evidence that taking Coenzyme Q10 by mouth for at least one week before Heart Bypass Surgery or Blood vessel surgery might help to reduce tissue damage. However, not all research agrees with this finding.
Taking Coenzyme Q10 by mouth daily appears to lower Systolic blood pressure in some people with high Systolic blood pressure but normal Diastolic blood pressure.
Taking Coenzyme Q10 by mouth seems to help prevent Migraine Headaches. Studies show it can decrease the frequency of Headaches by about 30% and the number of days with Headache-related Nausea by about 45% in adults. More than half of patients taking Coenzyme Q10 experience a 50% decrease in the number of Headache days per month. Taking Coenzyme Q10 also appears to reduce Migraine frequency in children who have low levels of Coenzyme Q10. It can take up to 3 months for significant benefit. It may take 3 months of treatment to see any benefit.
Taking Coenzyme Q10 by mouth seems to reduce tiredness and low mood in people with MS.
Taking coenzyme Q10 by mouth seems to improve physical performance in some people with Muscular Dystrophy.
When started within 72 hours of a heart attack and taken for one year, Coenzyme Q10 appears to lower the risk of Heart-related events, including another Heart attack.
Research shows that taking coenzyme Q10 improves erectile function in men with Painful Erections.
150-2400 mg per day.
150-160 mg per day, or 2 mg/kg per day. In some cases, doses may be gradually increased to 3000 mg per day.
A specific combination product containing 100 mg of Acetyl-L-Carnitine, 530 mg of Omega-3 Fatty Acids, and 10 mg of Coenzyme Q10, per day for one year.
A combination of 100 mg of Coenzyme Q10 twice per day plus 200 mcg of Selenium yeast per day for up to 5 years.
100 mg per day divided into two or three doses for up to 4 months or 2 mg/kg daily for up to one year.
400 mg per day for 12 weeks
300 mg daily for about 6 weeks. Also 200 mg of coenzyme Q10) plus 200 mg of ginkgo per day for 12 weeks.
100-200 mg per day for over 4 years.
150-300 mg per day in up to three divided doses for 1-2 weeks before surgery.
60 mg twice per day for 12 weeks.
100 mg three times per day, 150 mg once per day, or 100mg once per day for 3 months. A dose of 1-3 mg/kg per day for 3 months has also been used.
100 mg per day for 3 months.
500 mg twice daily for 3 months.
120 mg per day in two divided doses for up to one year. A combination of 100 mg of Coenzyme Q10 and 100 mcg of Selenium per day for up to one year has also been used.
300 mg per day for 6 months.
60-250 mg per day in up to three divided doses.
1-3 mg/kg daily for 3 months has been used in patients aged 3-18 years.
100 mg daily for 3 months in children aged 8-15 years.
Coenzyme Q10 is tolerated well in normal doses.
Mainly when taken on an empty stomach or when taken with less liquid than necessary – Headache, Dizziness, feeling sick, Constipation, Diarrhea, Stomach pain may occur.
Hypersensitivity Reactions (Rashes, Itching) may occur.
Coenzyme Q10 is POSSIBLY SAFE when taken by mouth appropriately during pregnancy. Coenzyme Q10 has been used safely when taken twice daily starting at 20 weeks until delivery. Not enough is known about the use of Coenzyme Q10 during Breast-feeding. Stay on the safe side and avoid use.
People undergoing Chemotherapy with a class of drugs called Alkylating agents should use Coenzyme Q10 with caution. There is some concern that Coenzyme Q10 might lower the effectiveness of these drugs. Some Alkylating agents include Busulfan, Carboplatin, Cisplatin, Cyclophosphamide, Dacarbazine, Thiotepa, and many others.
Coenzyme Q10 might lower blood pressure. It can increase the effects of medications used to lower blood pressure. Discuss your use of coenzyme Q10 with your healthcare provider if you have blood pressure problems.
Cigarette smoking depletes the amount of Coenzyme Q10 stored by the body.
Coenzyme Q10 might interfere with blood pressure control during and after surgery. Stop using Coenzyme Q10 at least two weeks before a scheduled surgery.